2021
October 04,2021
Publication
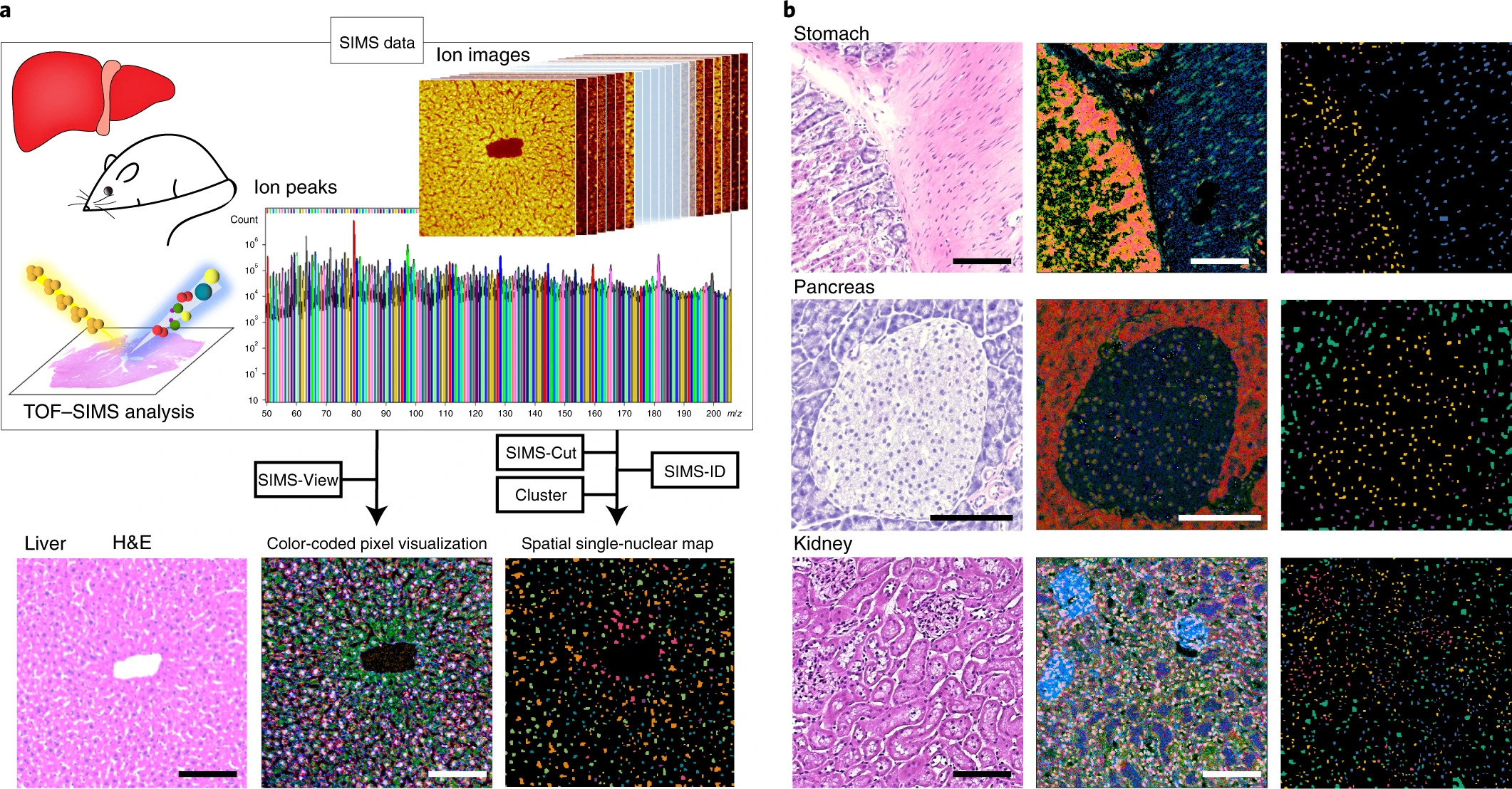
SEAM is a spatial single nuclear metabolomics method for dissecting tissue microenvironment
Spatial metabolomics can reveal intercellular heterogeneity and tissue organization. Here we report on the spatial single nuclear metabolomics (SEAM) method, a flexible platform combining high-spatial-resolution imaging mass spectrometry and a set of computational algorithms that can display multiscale and multicolor tissue tomography together with identification and clustering of single nuclei by their in situ metabolic fingerprints. We first applied SEAM to a range of wild-type mouse tissues, then delineated a consistent pattern of metabolic zonation in mouse liver.
LEARN MORE>>
张奇伟/张新荣/陈阳开发出单细胞空间代谢组分析新方法
LEARN MORE>>
July 20, 2021
Publication
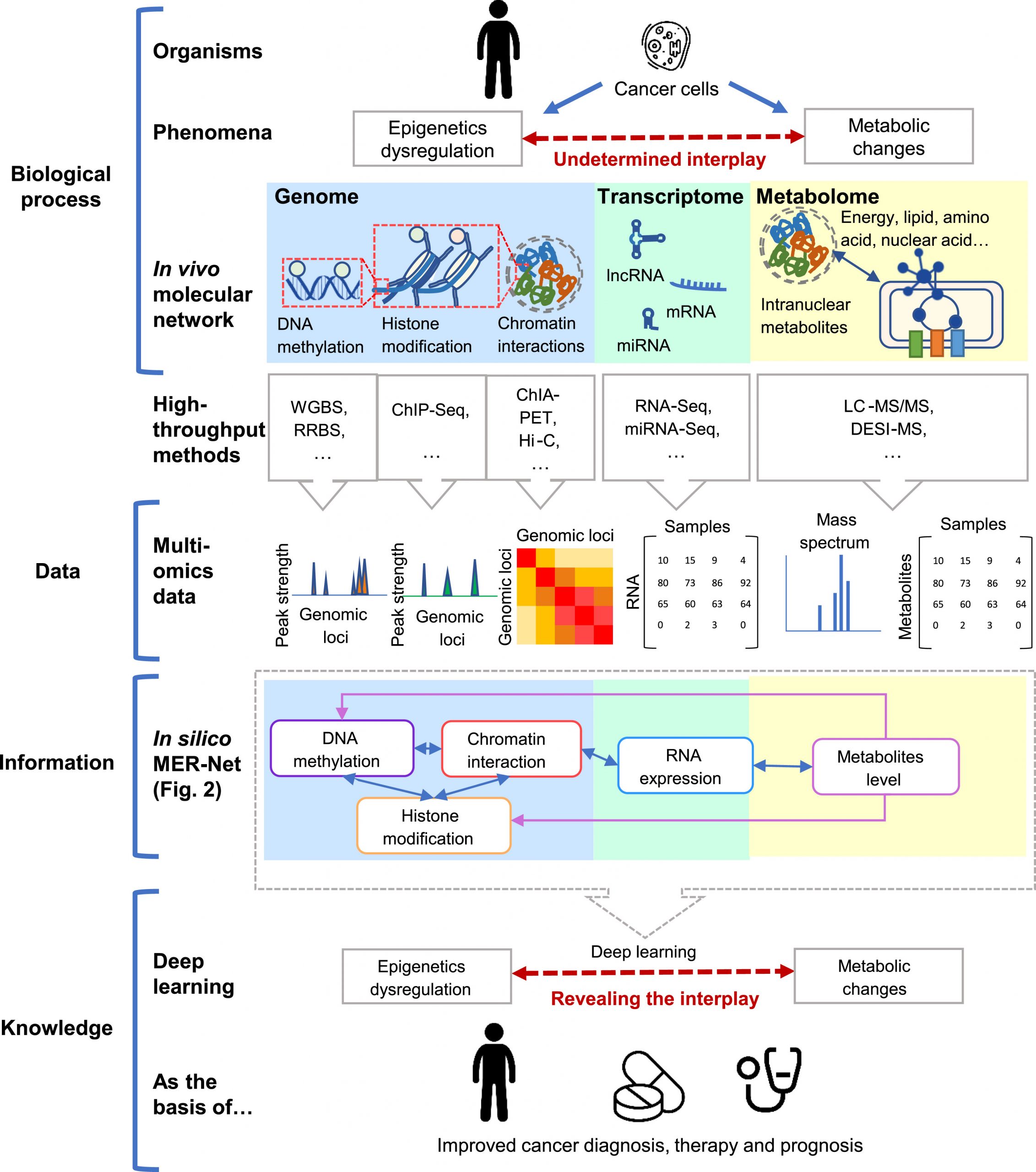
Multi-omics Metabolic and Epigenetics Regulatory Network in Cancer: A Systems Biology Perspective
Genetic, epigenetic, and metabolic alterations are all hallmarks of cancer. However, the epigenome and metabolome are both highly complex and dynamic biological networks in vivo. The interplay between the epigenome and metabolome contributes to a biological system that is responsive to the tumor microenvironment and possesses a wealth of unknown biomarkers and targets of cancer therapy.
LEARN MORE>>
JGG | 综述:癌症中的代谢和表观遗传学调控网络(MER-Net)
LEARN MORE>>
August 17, 2021
Publication
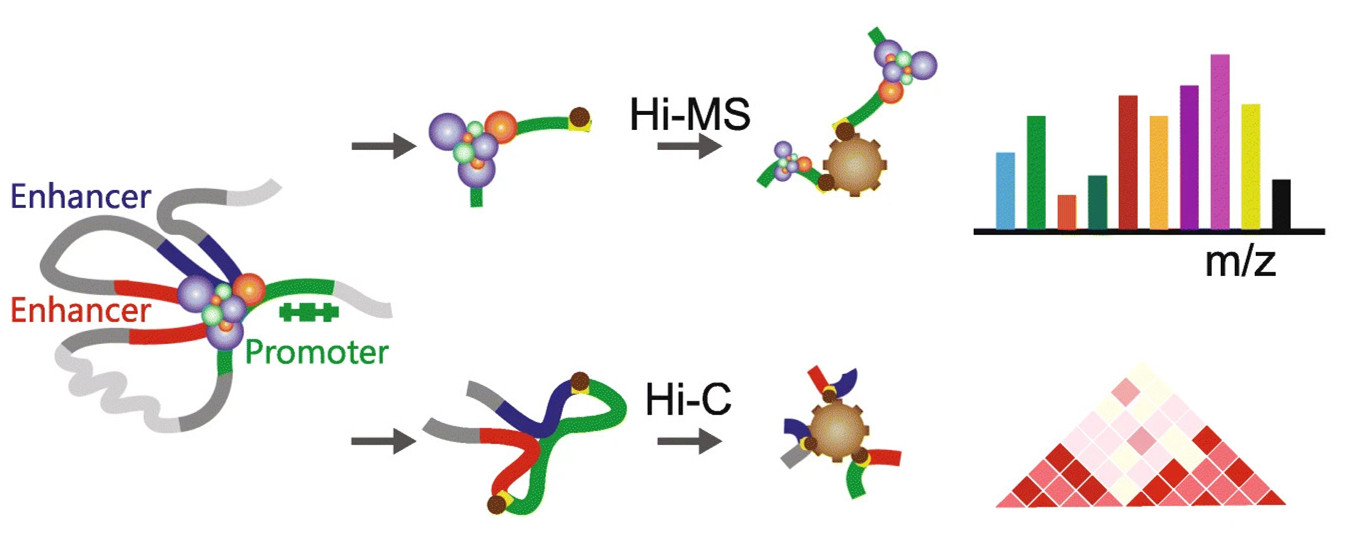
Quantifying the phase separation property of chromatin-associated proteins under physiological conditions using an anti-1,6-hexanediol index
Here, by combining chromatin-associated protein pull-down, quantitative proteomics and 1,6-hexanediol (1,6-HD) treatment, we develop Hi-MS and define an anti-1,6-HD index of chromatin-associated proteins (AICAP) to quantify 1,6-HD sensitivity of chromatin-associated proteins under physiological conditions.
LEARN MORE>>
张奇伟/师明磊/李婷婷/陈阳团队开发出定量测定生理条件下染色质相关蛋白相分离特性的新方法
LEARN MORE>>